food protein-induced enterocolitis syndrome a review of the new guidelines
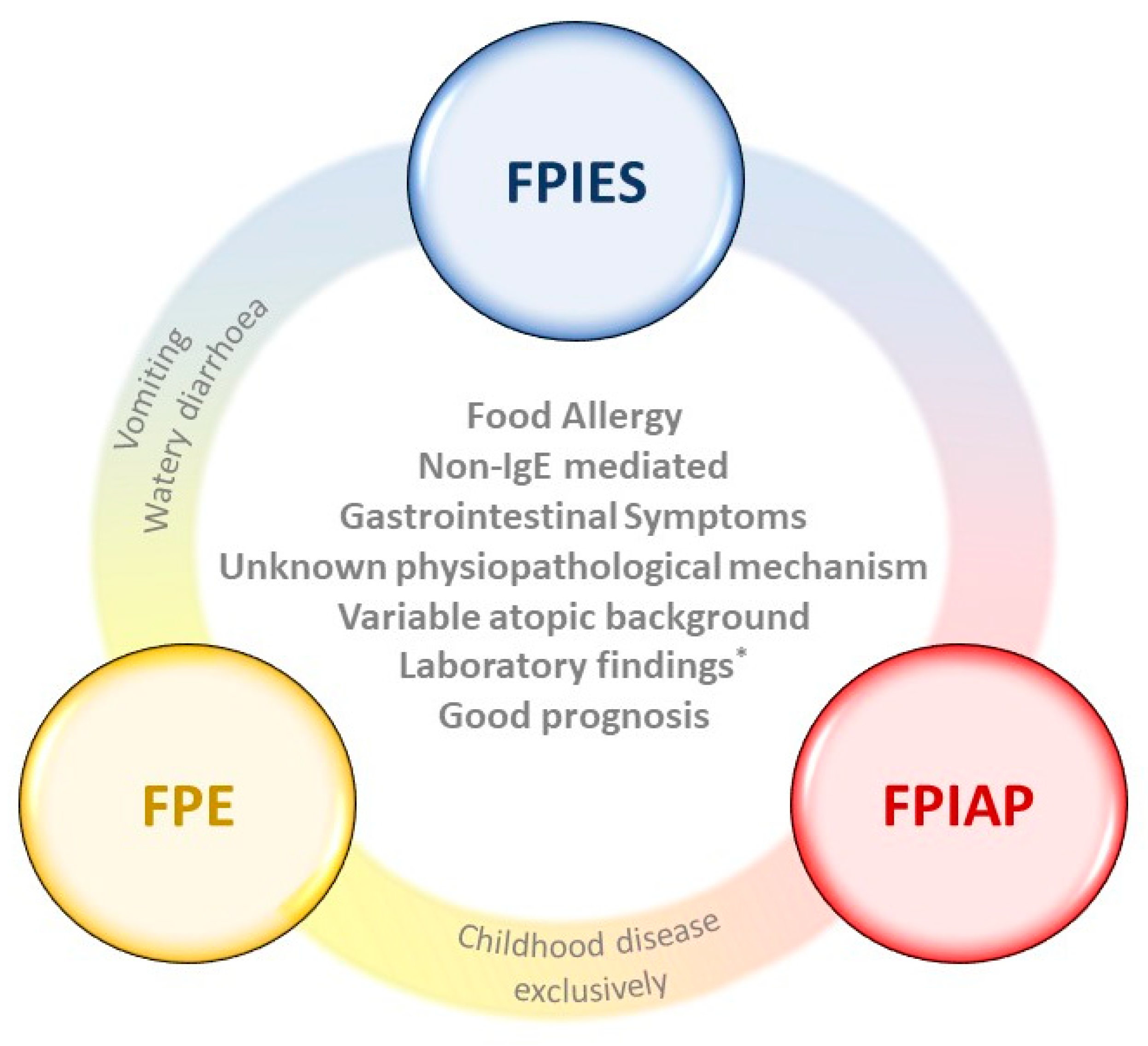
Non-IgE cell-mediated food allergic disorders encompass food protein-induced enterocolitis syndrome FPIES food protein-induced allergic proctocolitis FPIAP food protein-induced enteropathy Heiners syndrome pulmonary hemosiderosis celiac disease and cows milk CM protein-induced iron deficiency anemia. The aim of this review is to provide a case driven presentation of the presenting features and diagnostic criteria particularly focusing on the management of FPIES.

Clinical Types Of Food Protein Induced Enterocolitis Syndrome Fpies Download Scientific Diagram
The first International Consensus Guidelines for the Diagnosis and Management of Food Proteininduced Enterocolitis Syndrome were published in 2017 and reviewed epidemiology clinical presentation and prognosis of acute and chronic FPIES.
. Cells of the innate immune system appear to be activated during an FPIES reaction. First described in the mid 20th century it was just in the last decade that diagnostic and treatment guidelines for food protein-induced enterocolitis syndrome FPIES were established. And clinical outcomes are poorly established.
The workgroup outlined clinical phenotypes proposed diagnostic criteria and made recommendations on management. Cells of the innate immune system appear to be activated during an FPIES reaction. 3 Diagnosis of FPIES is difficult.
Food protein-induced enterocolitis syndrome FPIES is a non-IgE-mediated gastrointestinal food allergic disorder that has gained a major interest the past decade. Food protein-induced enterocolitis syndrome FPIES is a non-IgE mediated food allergy presenting in infants younger than 12 months. The workgroup outlined clinical phenotypes proposed diagnostic criteria and made recommendations on.
The first International Consensus Guidelines for the Diagnosis and Management of Food Proteininduced Enterocolitis Syndrome were published in 2017 and reviewed epidemiology clinical presentation and prognosis of acute and chronic FPIES. It also summarises the natural history and resolution of cows milk induced FPIES. Awareness of the diagnosis is improving and.
Food protein-induced enterocolitis syndrome FPIES is a severe presentation of non-IgE-mediated food allergy affecting the gastrointestinal GI tract mainly in infants and young children. The first International Consensus Guidelines for the Diagnosis and Management of Food Proteininduced Enterocolitis Syndrome were published in 2017 and reviewed epidemiology clinical presentation and prognosis of acute and chronic FPIES. Food proteininduced enterocolitis FPIES is a non-IgE cell-mediated food allergy that can be severe and lead to shock.
Acute FPIES typically presents between one and 4 hours after in -. High-quality studies providing insight into the pathophysiology diagnosis and management are lacking. 12 This syndrome is typically characterized by profuse vomiting and lethargy occurring classically 14 hours after ingestion of the offending food.
The first International Consensus Guidelines for the Diagnosis and Management of Food Protein-induced Enterocolitis Syndrome were published in 2017 and reviewed epidemiology clinical presentation and prognosis of acute and chronic FPIES. Seafood-induced FPIES may start in adulthood. The workgroup outlined clinical phenotypes proposed diagnostic criteria and made recommendations on management.
Food protein-induced enterocolitis syndrome FPIES is a severe presentation of non-IgE-mediated food allergy affecting the gastrointestinal GI tract mainly in infants and young children. Up to 10 cash back Food protein-induced enterocolitis syndrome FPIES is a non-IgE-mediated food allergy that has been well-characterized clinically yet it is still poorly understood. 12 Because celiac disease is traditionally.
Acute FPIES typically presents between one and 4 hours after ingestion of the trigger food with the principal. 3 Diagnosis of FPIES is difficult. 18 rows The first International Consensus Guidelines for the Diagnosis and Management of Food.
Reactions are characterized by the delayed onset of gastrointestinal symptoms predominantly repetitive vomiting which is often severe and should be considered a medical emergency. Up to 10 cash back Food protein-induced enterocolitis syndrome FPIES is an increasingly recognized non-immunoglobulin E IgE-mediated reaction to food. The workgroup outlined clinical phenotypes proposed diagnostic criteria and made recommendations on.
Food protein-induced enterocolitis syndrome FPIES is a non-IgE- cell-mediated food allergy of unknown prevalence and pathophysiology. FPIES prevalence which still needs to be accurately determine in different populations appears to be higher than previously thought ie up to 07 in infants in the 1st year of life. Acute FPIES manifests within 1-4 hours after ingestion with repetitive emesis pallor and lethargy progressing to dehydration and.
Acute FPIES is characterized by vomiting 14h andor diarrhea within 24h after ingestion of a culprit food. The first International Consensus Guidelines for the Diagnosis and Management of Food Protein-induced Enterocolitis Syndrome were published in 2017 and reviewed epidemiology clinical presentation and prognosis of acute and chronic FPIES. Food protein-induced enterocolitis syndrome FPIES is a poorly understood non-IgE gastrointestinal-mediated food allergy that predominantly affects infants and young children.
Onset is typically during the first year of life. 1 2 This syndrome is typically characterized by profuse vomiting and lethargy occurring classically 14 hours after ingestion of the offending food. Despite the potential seriousness of reactions awareness of FPIES is low.
5 rows Food protein-induced enterocolitis syndrome FPIES is a non-IgE mediated food allergy. Food proteininduced enterocolitis syndrome FPIES is a poorly understood nonIgE gastrointestinalmediated food allergy that predominantly affects infants and young children.

Interpretation Of The Food Protein Induced Enterocolitis Syndrome Oral Download Table

Management Of Acute Food Protein Induced Enterocolitis Syndrome Emergencies At Home And In A Medical Facility Annals Of Allergy Asthma Immunology

Advances In Understanding Immune Mechanisms Of Food Protein Induced Enterocolitis Syndrome Annals Of Allergy Asthma Immunology

Clinical Types Of Food Protein Induced Enterocolitis Syndrome Fpies Download Scientific Diagram

References In Immunopathophysiology Of Food Protein Induced Enterocolitis Syndrome Journal Of Allergy And Clinical Immunology

Food Protein Induced Enterocolitis Syndrome Oral Food Challenge Annals Of Allergy Asthma Immunology
Food Protein Induced Enterocolitis Syndrome As A Cause For Infant Hypotension The Western Journal Of Emergency Medicine

Gastrointestinal Immunopathology Of Food Protein Induced Enterocolitis Syndrome And Other Non Immunoglobulin E Mediated Food Allergic Diseases Sciencedirect

References In Food Protein Induced Enterocolitis Syndrome Not So Rare After All Journal Of Allergy And Clinical Immunology

Oral Food Challenge In Food Protein Induced Enterocolitis Syndrome Download Table

International Consensus Guidelines For The Diagnosis And Management Of Food Protein Induced Enterocolitis Syndrome Executive Summary Workgroup Report Of The Adverse Reactions To Foods Committee American Academy Of Allergy Asthma Immunology Journal

Foods Free Full Text Non Ige Mediated Gastrointestinal Food Protein Induced Allergic Disorders Clinical Perspectives And Analytical Approaches Html
Food Protein Induced Enterocolitis Syndrome Fpies And Nutrition

A Slice Of Food Protein Induced Enterocolitis Syndrome Fpies Insights From 441 Children With Fpies As Provided By Caregivers In The International Fpies Association The Journal Of Allergy And Clinical Immunology In
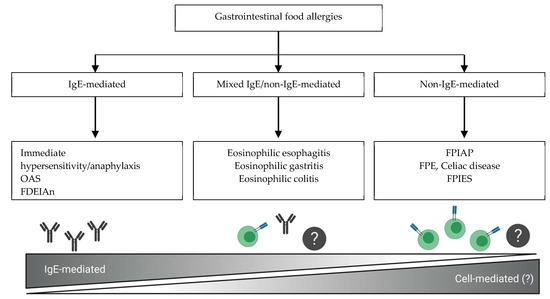
Nutrients Free Full Text Non Ige Mediated Gastrointestinal Food Allergies In Children An Update Html
Pdf Food Protein Induced Enterocolitis Syndrome A Review Of The New Guidelines

Food Protein Induced Enterocolitis Syndrome The Journal Of Allergy And Clinical Immunology In Practice

Food Protein Induced Enterocolitis Syndrome Annals Of Allergy Asthma Immunology